Table of Contents
New Features & Highlights
GAMS Studio
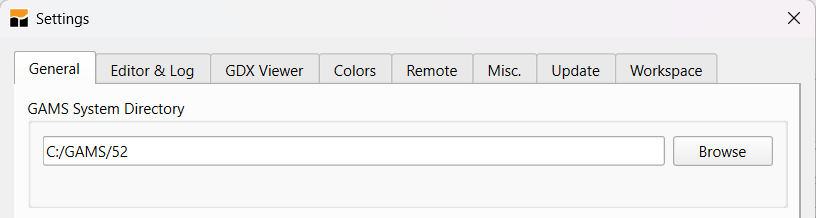
Select GAMS installation
It is now possible to select the GAMS installation to be used in GAMS Studio. There are two ways to set the path to GAMS:
- Using the command line parameter
--gams-dir. - In the
Settingson theGeneralpage.
In both cases the path is stored in the GAMS Studio settings and used for the next start.
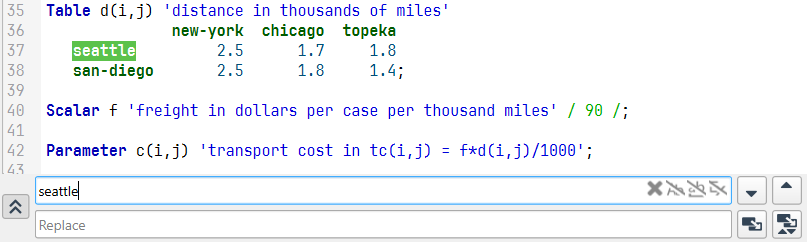
Quick Find and Replace
GAMS Studio now has a quick find option that is available with Ctrl+F (Command+F on macOS) in all text views. It uses F3 / Shift + F3 to find next / previous. It is bound to the current tab and changes its focus when switching to another tab. With Ctrl+R (Command+R on macOS) it additionally opens the replace section when the current editor isn't readonly.
The known complex search is still available with Shift+Ctrl+F (Shift+Command+F on macOS) and allows to search forward (F4) and backward (Shift+F4) in parallel independently from quick find.
Solver Lindo/LindoGlobal
Lindo Systems has released a new major version 16 of Lindo API. This new version promises a significant performance boost, allowing large linear models to solve up to 30% faster, integer problems 20% quicker, and previously "unsolvable" cases to be handled. Reliability for complex nonlinear problems, mathematical precision, and determinism of the solving process have been improved.
Solver SCIP
The newest major release of the SCIP Optimization Suite [96] has arrived in GAMS. From the many changes in SCIP 10, we highlight here three points that may be particularly interesting to GAMS/SCIP users:
- When solving NLPs or MINLPs, SCIP may call out to a local NLP solver to accelerate the search for a feasible solution. So far, the only NLP solver available in GAMS/SCIP was the high-performance interior point solver Ipopt. While usually a good choice, there can be instances where an active-set based method that can be warm-started is more efficient. Therefore, GAMS has contributed an interface to its solver CONOPT for SCIP version 10. For users with a GAMS/CONOPT license, GAMS/SCIP will now default to use CONOPT as NLP solver. Of course, the option to use Ipopt as NLP solver is still there and is not going away. To instruct GAMS/SCIP to use Ipopt, set parameter nlpi/ipopt/priority to 3000.
- SCIP has included a framework for Benders' Decomposition since version 6 (2018). We had not documented this for GAMS/SCIP, because solution values could be obtained for the variables of the master problem only so far. For version 10, GAMS contributed a new relaxator plugin to SCIP, which applies the decomposition on a copy of the problem and allows to retrieve solution values for all master and subproblem variables. To make use of Benders' Decomposition, decomposition information in form of the .stage attribute of variables (1 for the master variables, higher values for subproblems) needs to be provided and parameter decomposition/applybenders needs to be set to TRUE. Note that SCIP's Benders' Decomposition can only work efficiently when subproblems are continuous and recognized to be convex. The use of non-convex subproblems is still possible when all linking variables are of binary type, but may be inefficient.
- SCIP has gained the ability to compute irreducible infeasible subsets (IIS) of constraints of an infeasible problem, that is, a subset of constraints that cannot be satisfied, but that is feasible if any of the constraints in the IIS is dropped. IIS has proven to be a valuable tool when analyzing the infeasibility of a model instance and is available with many solvers. For SCIP, the computation of an IIS can be triggered by setting parameter gams/iis to 1 or 2.
53.1.0 Major release (February 16, 2026)
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank all of our users who have reported problems and made suggestions for improving this release. In particular, we thank Erling D. Anderson, Paul Buckland, Christophe Gouel, and Bruce McCarl.
GAMS System
GAMS
- Improved performance of the execution backend connection to GAMSPy by caching option definitions.
- Improved error reporting for $gdxLoadAll to write more information to the lst file.
- Fixed calculation of maintenance expiration date.
- Fixed GAMS execution backend crash when a GAMSPy model uses embedded code ReSHOP through a GAMS code block when ReSHOP solver is not installed.
GAMS Connect
- New allowed value
rangefor ExcelWriter option clearSheet. - Validate and raise error when using
schemaNamein SQLWriter with incompatible databases. - Fixed CSVReader failing on empty data.
- Fixed the Projection agent dropping special values
NAandUNDFin some cases.
Solvers
- The solve trace feature of some solver links has been extended to write an additional record with
Iidentifier when an improving feasible solution has been found. These lines are enabled by default, and their appearance can be controlled via a solver link optionsolvetraceincumbentormiptraceincumbentfor AlphaECP, CBC, COPT, CPLEX, GUROBI, HiGHS, SBB, SCIP, and XPRESS. The option specifies the minimal absolute change in the primal bound to trigger writing theIline and is set to 10-6 by default.
CPLEX
- Readded options miptracenode and miptracetime.
EXAMINER
- Updated the tracefile writing facility to be more robust and flexible.
- Polished the output in many small ways.
- The hidden solver Examiner2 will be removed in a future release.
GUROBI
- New libraries 13.0.1.
- Fixed option freegamsmodel.
- Fixed option concurrentmethod.
- Fixed sensitivity of objective function.
- Fixed model status in case of an infeasible model with no solution.
HiGHS
- Added support for CUDA 13 for running cuPDLP-C on GPUs.
KNITRO
- New libraries 15.1.0.
- Performance improvements when using the Augmented Lagrangian (AL) algorithm (nlp_algorithm = 6).
- New option presolveop_clique_merging: Determine whether or not to enable the Knitro presolve operations that attempt to merge cliques to strengthen the formulation.
- New option presolveop_probing: Determine whether or not to enable the Knitro presolve operations that analyze deductions made by fixing integer variables.
- New option mip_heuristic_fixpropagate: Specifies whether or not to enable the MIP fix-and-propagate heuristic.
- New option writeprob: Writes problem to file (format based on extension).
- Changed default of option ftol to 1e-12.
LINDO/LINDOGLOBAL
- New libraries 16.0.110.
- Faster Linear Solver:
- Simplex solvers solve large linear models an average of 25-30% faster.
- Integer Solvers Improvements:
- New heuristics help find good quality solutions for previously unsolvable instances.
- An average of 15-20% faster to optimality due to enhancements in re-optimizations and 20% more instances solved to optimality on Lindo's standard benchmark suite.
- Nonlinear and Global Solver Enhancements:
- Superior performance on difficult nonlinear problems due to improved recovery strategies.
- Improved Multi-Start solver based on entropy maximization.
- Improved linearization process and recognition of common terms.
- Tighter linear relaxations by incorporation of variable bounds.
- Global solver solution path repeatability improved.
- Faster Linear Solver:
MOSEK
- New libraries 11.1.5.
- Updated automatic choice of number of threads to not use more than 32 threads.
- Reduced memory consumption of graph partitioning based ordering method of the interior-point optimizer when employing more than 8 threads.
- When solving a mixed-integer problem with all discrete variables fixed (solvefinal), the right-hand-sides of all linear equations and variable bounds are now adjusted such that the solution of the mixed-integer problem satisfies all linear constraints, independent of feasibility tolerances. This increases the chance that the fixed problem can be solved successfully.
NLPEC
- Fix a failure in case of refType set to "median" and a doubly-bounded variable whose upper bound is negative.
SCIP Optimization Suite
- New libraries PaPILO 3.0.0.
- Improved dominated columns presolve by applying topological compression on column domination arcs.
- New parallelized clique merging presolver.
- New libraries SoPlex 8.0.1.
- New libraries SCIP 10.0.1.
- Presolve:
- Implicit integrality of variables is now distinguished into strong and weak types, depending on whether integrality is implied for all feasible or only at least one optimal solution.
- A new presolver "implint", which detects implied integral variables by detecting (transposed) network submatrices in the problem, has been added (currently disabled by default). New parameters presolving/implint.
- Changed defaults of presolving/restartminred and presolving/immrestartfac from 0.1 to 0.05.
- PaPILO's clique merging presolver is now available:
- New parameter presolving/milp/enablecliquemerging: whether to enable clique merging in PaPILO.
- New parameter presolving/milp/maxedgesparallel: maximal number of edges in the parallel clique merging graph.
- New parameter presolving/milp/maxedgessequential: maximal number of edges in the sequential clique merging graph.
- New parameter presolving/milp/maxcliquesize: maximal size of cliques considered for clique merging.
- New parameter presolving/milp/maxgreedycalls: maximal number of greedy max clique calls in a single thread.
- Symmetry Handling:
- More techniques to handle reflection symmetries have been added, in particular, for orbitopes with column reflections and matrices whose rows and columns can be permuted by a symmetry.
- New parameter propagating/symmetry/handlesignedorbitopes: whether to apply special symmetry handling techniques for orbitopes whose columns can be (partially) reflected.
- New parameter propagating/symmetry/usesimplesgncomp: whether symmetry components all of whose variables are simultaneously reflected by a symmetry shall be handled by a special inequality.
- The orbitopes constraint handler has been split into different handlers for full orbitopes and packing/partitioning orbitopes to reduce memory use. Replaced
constraints/orbitopeparameters by parameters constraints/orbitope_full and constraints/orbitope_pp. - Symmetry detection no longer treats implicit integer variables separately, but computes symmetries based on the variable type inferred from variable bounds and implied integrality.
- Removed value for implied integer variables from bitset parameter propagating/symmetry/sstleadervartype: upper bound changed from 15 to 7, default changed from 14 to 6.
- The symmetry detection graphs have been simplified for the case where all edges have the same color.
- Replaced parameters
propagating/symmetry/nautymaxncellsandpropagating/symmetry/nautymaxnnodesby new parameter propagating/symmetry/nautymaxlevel to limit depth of Nauty's search tree. - New parameter propagating/symmetry/dispsyminfo: whether to print information about applied symmetry handling methods.
- New parameter propagating/symmetry/maxnnewivolus.
- More techniques to handle reflection symmetries have been added, in particular, for orbitopes with column reflections and matrices whose rows and columns can be permuted by a symmetry.
- Cutting Planes:
- A new separator "flower" to generate flower cuts from AND constraints and nonlinear product expressions has been added. New parameters separating/flower.
- Primal Heuristics:
- A new decomposition kernel search (DKS) heuristic has been added (disabled by default). It can be used both as a construction heuristic as well as an improvement heuristic. Existing decomposition information can be utilized. New parameters heuristics/dks.
- Tuned several primal heuristics:
- Changed default of heuristics/crossover/freq from 30 to 15.
- Changed default of heuristics/gins/freq from 20 to 10.
- Changed default of heuristics/randrounding/freq from 20 to 10.
- Changed default of heuristics/rins/freq from 25 to 15.
- Changed default of heuristics/shifting/freq from 10 to 5.
- Changed default of heuristics/adaptivediving/maxlpiterquot from 0.1 to 0.15.
- Changed default of heuristics/conflictdiving/maxlpiterquot from 0.15 to 0.05.
- Changed default of heuristics/feaspump/maxlpiterquot from 0.01 to 0.05.
- Changed default of heuristics/objpscostdiving/maxlpiterquot from 0.01 to 0.05.
- Removed parameter
heuristics/scheduler/heurtimelimit.
- Branching:
- A new dynamic max-lookahead criterion for strong branching has been added: a probability distribution is fitted to the observed candidate gains and evaluating further candidates stops when the expected tree-size reduction no longer justifies the LP evaluation cost.
- New parameters branching/relpscost/dynamiclookahead, branching/relpscost/dynamiclookaheadquot, branching/relpscost/dynamiclookdistribution, branching/relpscost/minsamplesize: enable flag, fraction threshold, distribution choice, and minimum sample size.
- Pseudocost have been extended to approximate the longer-term influence of a branching decision by aggregating improvements from subsequent levels, weighted by a discount factor.
- New parameter branching/collectancpscost: enable/disable recording of ancestral pseudo costs.
- New parameters branching/pscost/discountfactor and branching/relpscost/discountfactor: discount factors for ancestral pseudo costs in pseudocost-based branching rules.
- A new dynamic max-lookahead criterion for strong branching has been added: a probability distribution is fitted to the observed candidate gains and evaluating further candidates stops when the expected tree-size reduction no longer justifies the LP evaluation cost.
- Conflict Analysis:
- Added a generalized resolution conflict analysis that operates directly on linear constraints instead of conflict graphs. New parameters conflict/usegenres, conflict/reduction, conflict/mbreduction, conflict/maxvarsfracres, conflict/resfuiplevels, conflict/fixandcontinue, and SCIPconflict_maxcoefquot conflict/maxcoefquot "conflict/maxcoefquot".
- Changed upper bound of conflict/maxvarsfac from ∞ to 1.
- General conflict upgrades are now applied in the conflict store, and dualsol and dualray conflict upgrades are disabled.
- Nonlinearity:
- Added an interface to the NLP solver CONOPT. New parameters nlpi/conopt/priority and nlpi/all/priority.
- Extended second-order cone detection to simple bilinear constraints, e.g., \(x\cdot y \geq 1\).
- Benders' Framework:
- Added a relaxator benders that, given a problem and decomposition information, runs Benders' Decomposition in a sub-SCIP and returns a solution to the main SCIP.
- Infeasibility Analysis:
- Added the possibility to search for irreducible infeasible subsystems (IIS) and an IIS finder plugin greedy, which implements a greedy addition and deletion based algorithm with dynamic batch sizing.
- Miscellaneous:
- Restarts from within the branch-and-bound tree (after the root node) are now only applied if there have been global variable fixings.
- New parameter randomization/randomseedshiftmultiplier: multiplier for the shift set by randomization/randomseedshift. The shift is multiplied by (6*
randomseedshiftmultiplier+1), with the default value forrandomseedshiftmultiplierset to 10 now. This default value is expected to change with every major release. Setting the parameter to 0 restores SCIP 9 behavior. - Parameters
propagating/.../timingmaskcan now be set to 0 to disable a propagator completely. - Changed defaults of parameters constraints/components/propfreq and SCIPconstraints_components_maxdepth constraints/components/maxdepth "constraints/components/maxdepth" from 1 and -1 to -1 and ∞, respectively, to avoid unnecessary calls of components propagator by default.
- Changed default of constraints/and/upgraderesultant from true to false.
- New parameter lp/minsolvedepth: lower bound on the depth at which LPs are solved.
- Presolve:
- For more details, see the release report [96].
- GAMS/SCIP now defaults to use CONOPT as NLP solver, if the model instance fits into demo or community license limits or a GAMS/CONOPT license is available. To revert to use Ipopt (or IpoptH, if licensed), set parameter nlpi/ipopt/priority to 3000.
- Benders' Decomposition is now available in GAMS/SCIP. Use parameter decomposition/applybenders to solve a problem for which decomposition information has been provided with Benders' algorithm, see also Decomposition Information and Benders' Decomposition. Parameters of the Benders' framework are now documented in the SCIP options documentation.
- The computation of an IIS can now be triggered by setting option gams/iis to 1 or 2.
XPRESS
- Added option freegamsmodel.
- Changed behaviour of solution pool: XPRESS solution pool is now enabled if solnpoolCapacity is larger than 1. Previously it was enabled if solnpool or solnpoolmerge were set.
- Changed default solnpoolCapacity to 1.
- Fixed rare error when using the solution pool (solnpool or solnpoolmerge).
- Fixed model status in case of an infeasible model with no solution.
- Fixed options objnabstol and objnreltol to be string list options.
Tools
GAMS Studio
- New version 1.24.0:
- New Feature: Added a quick-find to the bottom of text editors for searching in the current file, called "find".
- The quick "find" is evoked with
Ctrl+F(Command+Fon macOS) and usesF3/Shift+F3to find next / previous. - With
Ctrl+R(Command+Ron macOS) it additionally opens the replace section when the current editor isn't readonly. - The complex "search" dialog is now evoked with
Shift+Ctrl+F(Shift+Command+Fon macOS) and usesF4/Shift+F4to search next / previous.
- The quick "find" is evoked with
- Added quick-find to Process Log, GAMS Release Notes, and Studio Changelog.
- Added GAMS system directory configuration to settings dialog to switch between different GAMS installations.
- Improved settings field for GAMS system directory.
- Added the search and replace configuration to the settings and restore the configuration when Studio is started.
- Translate UNC path to a local path for the license dialog, e.g., when the
Documentsfolder on Windows has been moved to a server. - More search improvements:
- Improved search and replace dialog selection behavior. Now the result selection is removed when the dialog is closed and no search result list is open.
- Improved search and replace file pattern, i.e., the default pattern has been changed from
*to*.gms. The change is applied to all the cases where a file pattern can be configured.
- Ensure listing files are closed on the file system when the corresponding tab is closed.
- Improved behavior of
--integrated-help=on/offcommand line option, to ensure the Help View is not unexpectedly disabled when started. - Show the LST line number in debug mode when the execution is paused. The information is visible at the very bottom of the debugger.
- Changed the start directory of the file open dialog to the base directory of the current project.
- Renamed 'Remove Project' to 'Close Project' in the Project Explorer context menu.
- Fixed the path to the main file when running MIRO. Before, the main file path always corresponded to the working directory.
- Fixed enabling of MIRO menu. Before, the MIRO menu was not enabled in some cases although a correct path has been configured.
- Fixed wildcard matching for the Model Library dialog, i.e., when wildcard matching was enabled not all models matching the pattern were listed.
- Fixed search and replace in Folder. Before, all files unknown to Studio have been ignored by the replace.
- New Feature: Added a quick-find to the bottom of text editors for searching in the current file, called "find".
MPS2GMS
- Removed support for creating
=c=equations.
APIs
GAMS Transfer Python
- Performance related enhancement when validating symbol order in a
Container. - Added support for pandas 3.0.0.
GDX
- New libraries 7.11.19.
GMO
- Previously, setting
gmoUseQtrue for linear models was not supported: several functions in the GMO API would treat this case as a fatal error or would behave in an undefined way. This has been adjusted: now reasonable outputs are efficiently provided in this case.